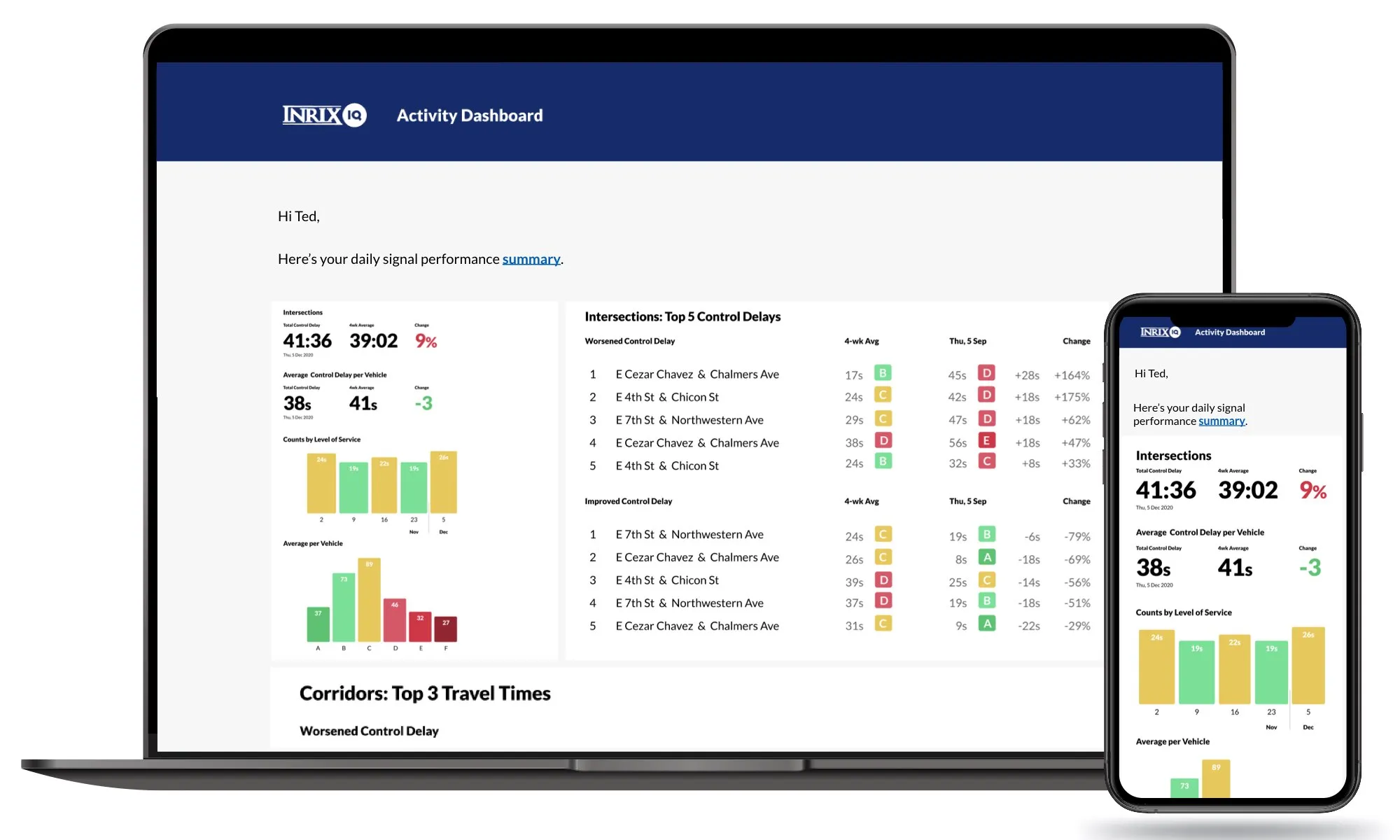
According to researchers at the University of Minnesota, most traffic signals in the US are only retimed every two to five years (or longer), largely due to the expense associated with retiming efforts. However, over the past several years, University of Minnesota researchers have developed and refined its SMART Signal system to make it easier and less expensive to retime signals.
The system, developed with funding from the Minnesota Department of Transportation (MnDOT), not only collects traffic and si
April 20, 2015
Read time: 2 mins
According to researchers at the 584 University of Minnesota, most traffic signals in the US are only retimed every two to five years (or longer), largely due to the expense associated with retiming efforts. However, over the past several years, University of Minnesota researchers have developed and refined its SMART Signal system to make it easier and less expensive to retime signals.
The system, developed with funding from the2103 Minnesota Department of Transportation (MnDOT), not only collects traffic and signal-phase data automatically, but it also identifies under-performing traffic signals and generates optimal signal timing plans with minimal human intervention.
MnDOT, along with many US cities and counties embeds loop detectors in roads that notify a traffic signal when a vehicle is present. Staff normally must manually track wait times to determine how signal timing is affecting traffic.
The researchers claim SMART Signal automates much of this process by recording how long a vehicle waits at an intersection and automatically reporting the data, along with signal timing, to a central server. The data, viewable in real-time on a website, —can then be analysed to determine traffic patterns and optimal signal timing. By reducing the cost of data collection and performance measurement, SMART Signal allows MnDOT to base signal retiming decisions on performance rather than a fixed schedule.
The latest research optimises the system’s ability to reduce traffic delays by developing a framework to diagnose problems that cause delays at traffic signals and an algorithm that automatically optimises the signal plan to address these problems.
The enhancements were successfully tested on Highway 13, reducing vehicle delay there by five per cent. Researchers say the benefit could be in the double digits for corridors with worse traffic delays.
The soft ware upgrade has since been integrated into the more than 100 intersections in Minnesota equipped with the SMART Signal system.
The system, developed with funding from the
MnDOT, along with many US cities and counties embeds loop detectors in roads that notify a traffic signal when a vehicle is present. Staff normally must manually track wait times to determine how signal timing is affecting traffic.
The researchers claim SMART Signal automates much of this process by recording how long a vehicle waits at an intersection and automatically reporting the data, along with signal timing, to a central server. The data, viewable in real-time on a website, —can then be analysed to determine traffic patterns and optimal signal timing. By reducing the cost of data collection and performance measurement, SMART Signal allows MnDOT to base signal retiming decisions on performance rather than a fixed schedule.
The latest research optimises the system’s ability to reduce traffic delays by developing a framework to diagnose problems that cause delays at traffic signals and an algorithm that automatically optimises the signal plan to address these problems.
The enhancements were successfully tested on Highway 13, reducing vehicle delay there by five per cent. Researchers say the benefit could be in the double digits for corridors with worse traffic delays.
The soft ware upgrade has since been integrated into the more than 100 intersections in Minnesota equipped with the SMART Signal system.