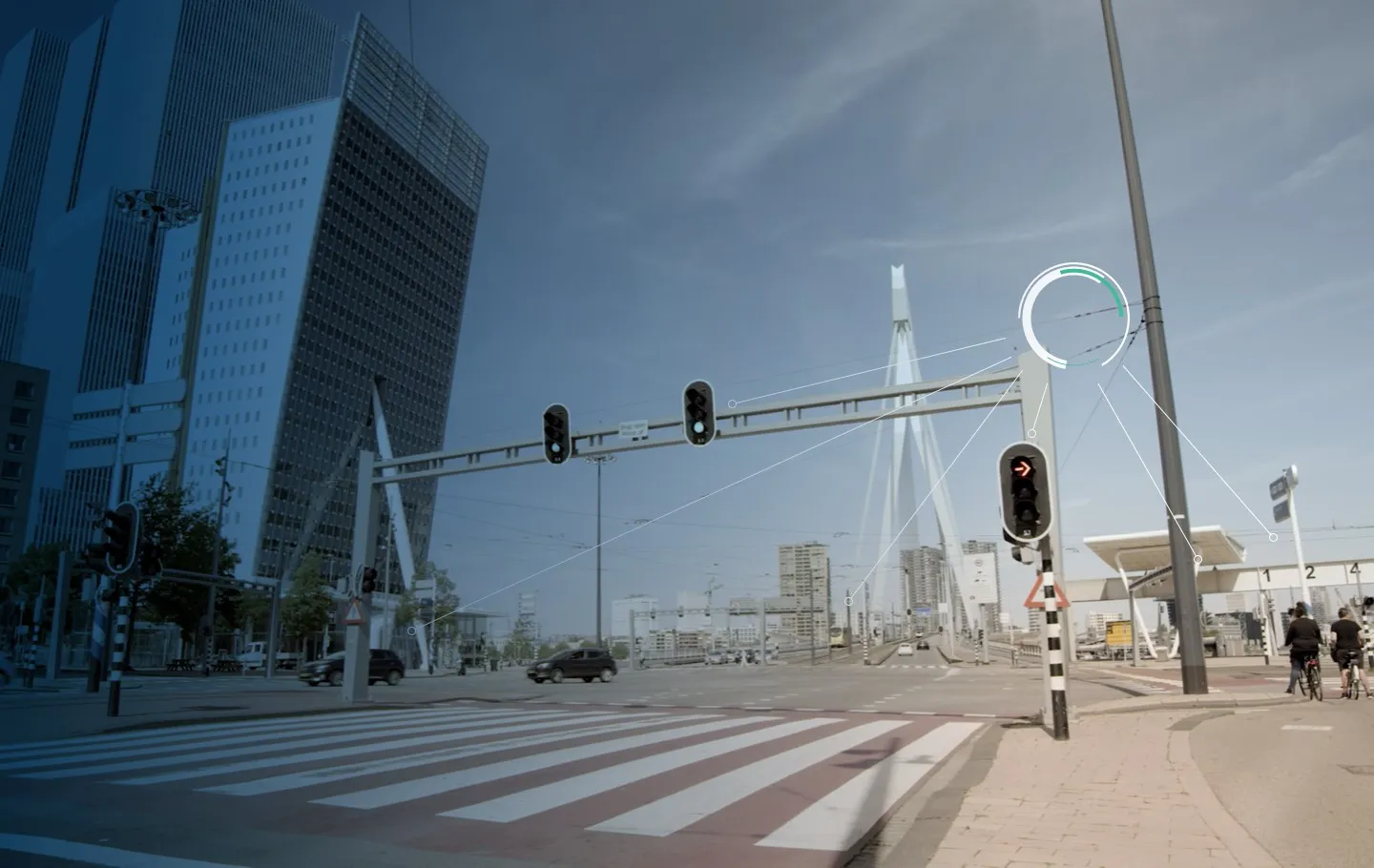
The Communities Against Rider Surveillance (CARS) says MDS is a data language that allows cities and vehicles to communicate in real time via an application programming interface (API) that sends details to cities about the start, end and route of each vehicle trip. A second API requires real-time pushing of precise rider locations to cities.
The coalition is calling on cities to reject MDS tracking programmes and adopt data collection policies that protect rider privacy and safety.
CARS spokesperson Keeley Christensen, says: “Imagine your personal movements being tracked by the government. Every time you visit the doctor, have a date or go to the gym, a government record would be created. Thanks to MDS, this scenario could soon become a reality. It’s not surprising that city planners have cut the public entirely out of the MDS conversation, but we hope that CARS will finally give them a voice.”
According to CARS, using MDS requires vehicles to transmit their precise location to cities which can then send instructions back to drivers – re-routing cars, limiting street access and imposing fines.
MDS does not collect the names of riders, but a Los Angeles Times report suggests that “someone with basic coding skills and access to the data could easily connect a trip to an individual person”.
This means MDS can be used to identify and reveal sensitive location information on riders such as business meetings, personal appointments and political activities, CARS adds.
The group recognises that while US cities are fighting hacking attempts and internal abuses of confidential data, but most have “failed to specify their policies and practices for handling MDS location data, let alone adopted clear privacy safeguards before implementing these tracking programmes”.
The Los Angeles Department of Transportation created MDS in 2018 to track and direct the movement of individual vehicles, ranging from dockless scooters and bikes to ride-hailing, commercial vehicles, autonomous cars, and drones.
Members of CARS include Uber, Patient Privacy Rights and a national civic engagement group dedicated to Latino and migrant communities called Mi Familia Vota.









