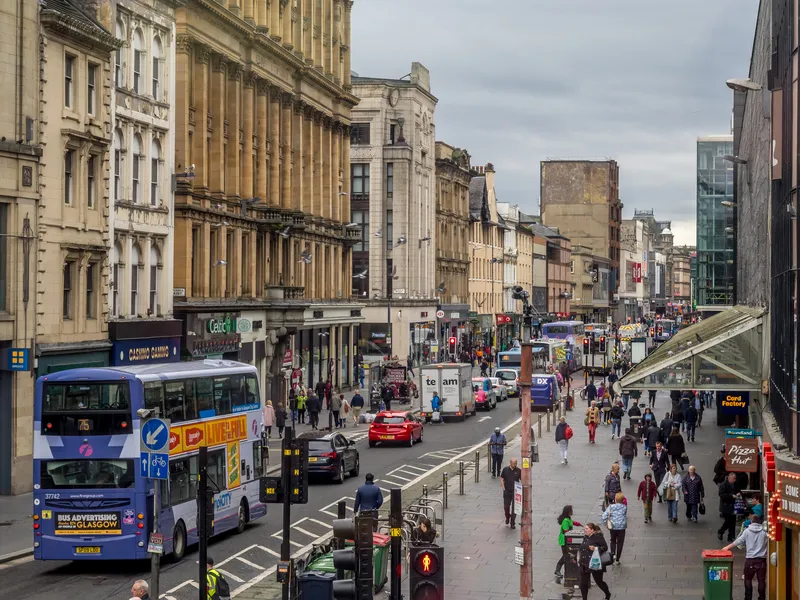
The city of Glasgow has put into place the final policy of its ambitious strategy to tackle carbon emissions and move away from a more car-dependent culture.
With this final phase of the transport strategy, the Spatial Delivery Framework, the Scottish city can take key decisions to influence travel behaviour and encourage a shift toward more sustainable forms of transport, such as buses, trains and active travel.
More bus priority corridors, park-and-ride areas and electric vehicle charging stations and mobility hubs are among the transport improvements that the city hopes can now take place in a way to benefit the most people.
Almost half the households in Glasgow do not have access to a car. However, according to UK Department for Transport (DfT) figures, 2.17 billion vehicle-kilometres were travelled in Glasgow in 2022 - the largest distance for any local authority area in Scotland. The strategy aims to cut this by 30% by 2030 - ahead of the national target of reducing kilometres travelled by 20% by 2030.
"This has been a huge undertaking that has generated over one hundred policy objectives that will ultimately transform transport and travel in the city,” said councillor Angus Millar, the city convenor for transport and who leads on the city's journey to Net Zero.
“At the core of our plans is a recognition that we must reduce how much we rely on private vehicles for transport. There are far more sustainable and equitable modes of transport than the car and we must make space for alternative, more efficient ways of getting about Glasgow.”
He said initiatives such as bus priority corridors, new park and ride stations and mobility hubs “are the kind of interventions that makes the bus a more attractive option and encourage drivers to leave their vehicles behind because the network supports integrated travel choices”.
Development of the framework has already helped to identify 16 potential bus priority corridors throughout the city and possible routes for the bus network. Orbital routes in Glasgow's East End, a route between Glasgow South, Paisley and Glasgow Airport and an orbital route between Partick and Springburn are being considered.
In addition to the nine park and ride stations already in Glasgow, the framework has highlighted seven further possible areas close to the city boundary. Areas for possible mobility hubs where multiple modes of transport could intersect, have also been mapped out.
Other transport improvements or interventions include the City Network for Active Travel, the Liveable Neighbourhoods programme, freight hubs, electric vehicle charging stations, parking zones and prioritising local access where road space is constrained.