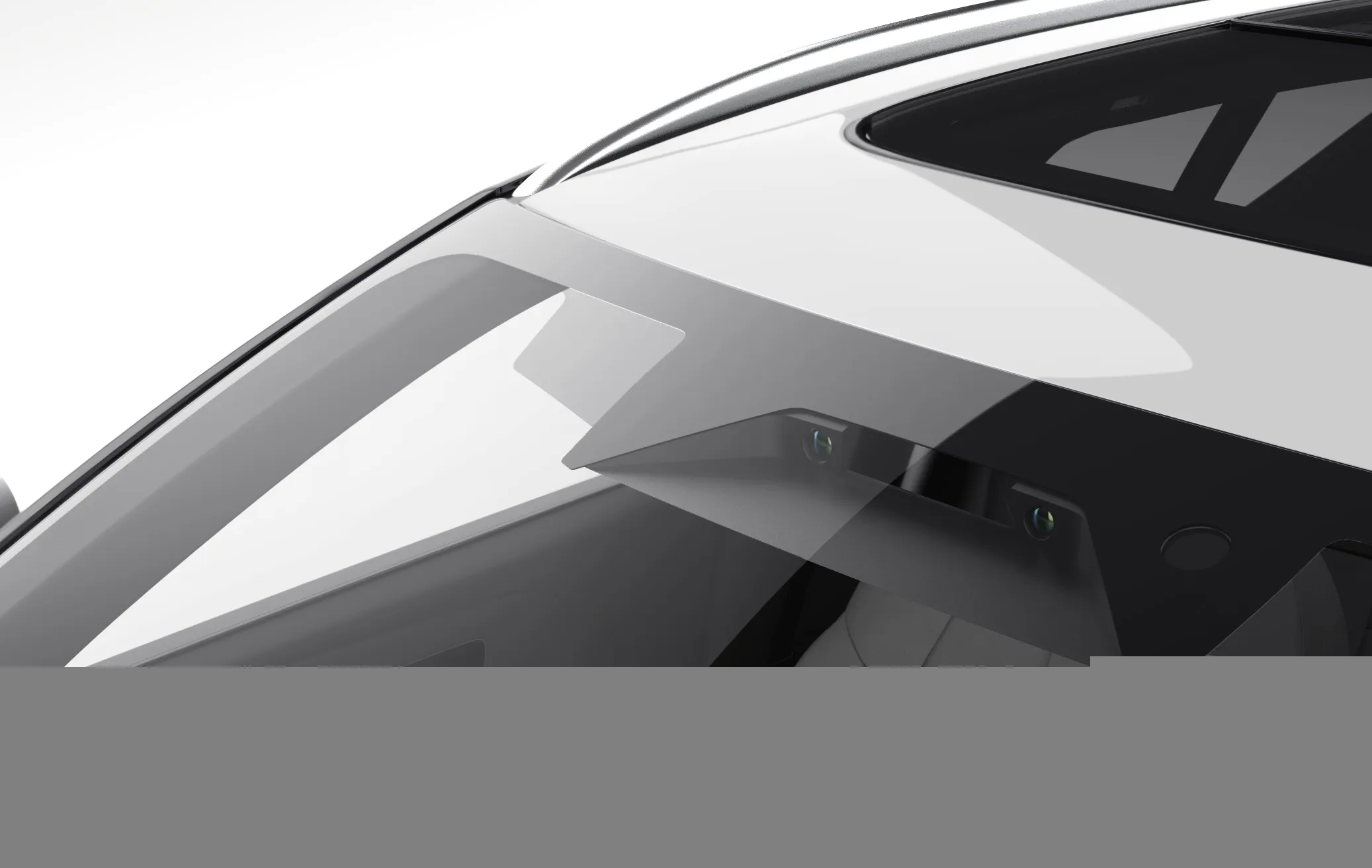
Seyond - formerly called Innovusion – and Wideye have launched a Lidar solution that sits behind the windscreen of vehicles.
A fully-functional prototype of their in-cabin Lidar was highlighted at this week's Consumer Electronics Show (CES) in Las Vegas. It featured a full-size Wideye windshield and Seyond's operational Robin-E Lidar solution, complemented by additional sensors such as cameras and rain-detection technology.
The companies said that the windshield remains an obvious location for a Lidar sensor in vehicle integration, given its high mounting position and low impact on vehicle design and its ability to protect sensors from the external environment.
Seyond and Wideye have collaborated to solve major hurdles for in-cabin integration such as limiting performance drop with windshield installation angle and having an adequate heat and noise profile in a small form factor.
Seyond is a global provider of high-performance Lidar sensors and solutions for autonomous vehicles and smart transportation. Wideye, a corporate scale-up of Tokyo-based glass firm AGC Group, specialises in glass solutions for optical sensor integration.
Junwei Bao, chief executive at Seyond, says: "This feature is the next step in our goal to provide safer, smarter transportation across the globe and we look forward to continued partnership and innovation with Wideye."
"This is not the first time that we are developing and showcasing Lidar integration behind the windshield, "said Gaetan Friart, chief executive at Wideye. "Our vision has always been to have this in-vehicle Lidar integration case as mainstream. However, whereas our previous efforts primarily aimed at demonstrating the feasibility of such a solution, this time we're unveiling a product that's closer than ever to being market-ready.”
Seyond, based in California, develops Lidar solutions for autonomous driving and smart infrastructure development. The company's portfolio includes ultra-long range flagship Lidar sensor Falcon, mid-to-short range Lidar sensor Robin and perception service software platform OmniVidi. These power automotive and ITS solutions for partners such as Nio, Faraday Future, Exwayz and Hexagon. Currently, over 200,000 Falcon units are in use.
Wideye is backed by AGC Automotive Europe, AGC Group's European automotive glass branch, which specialises in the production of glazing solutions for carmakers. Since its launch in 2016, Wideye has focused on enabling ADAS deployment and making fully autonomous vehicles a reality.