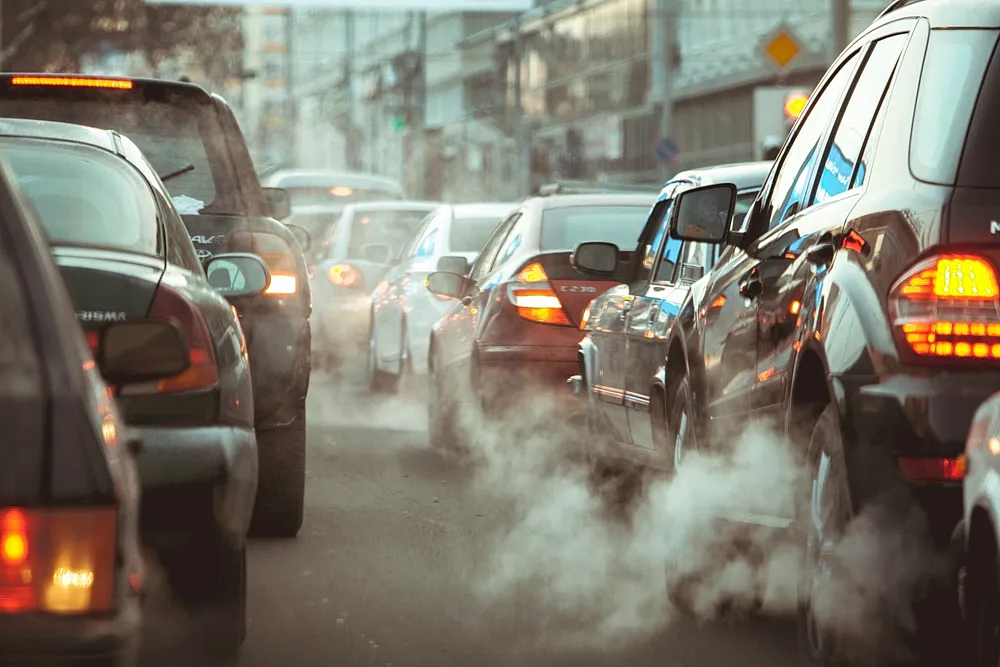
As part of its drive to create a greener, healthier city, Westminster City Council in London is set to trial emissions-based charging for diesel cars parking within Marylebone.
In a pilot programme to be introduced from 3 April 2017, the charge for pay-to-park bays during normal parking hours will be raised specifically within F zone for diesel cars, some of the heaviest of polluting vehicles. This will apply to visitors into Marylebone, with resident permits remaining unchanged.
The surcharge will ad
January 30, 2017
Read time: 2 mins
As part of its drive to create a greener, healthier city, Westminster City Council in London is set to trial emissions-based charging for diesel cars parking within Marylebone.
In a pilot programme to be introduced from 3 April 2017, the charge for pay-to-park bays during normal parking hours will be raised specifically within F zone for diesel cars, some of the heaviest of polluting vehicles. This will apply to visitors into Marylebone, with resident permits remaining unchanged.
The surcharge will add 50 per cent to the current rate of £4.90 per hour in F Zone. Customers are currently able to Park and Pay per minute up to a maximum of 240 minutes (4 hours), meaning charges will be 8p per minute in real terms and 12p per minute for diesels.
Marylebone suffers some of the highest pollution levels in London, given the area’s location, mix of land uses, building density and type, and number of vehicle trips. The ‘polluter pays’ principle aims to reduce harmful vehicle emissions in Marylebone and any money raised will be spent on initiatives to promote sustainable transport.
Marylebone’s location between major transport routes results in a complex urban air quality problem with levels of nitrogen dioxide that exceed recommended health levels and very high levels of particulate matter.
The council believes the pilot surcharge for diesel will also provide valuable insight into how the policy works practically and whether there are positive behavioural changes from it that could be replicated elsewhere.
In 2017, Westminster will also see several green initiatives come into effect in the low emission neighbourhood which will help improve air quality. This includes freight consolidation and a new EV infrastructure with charging points upgraded and increased by up to 20 new outlets, including some rapid chargers. The council is also encouraging more sustainable transport.
In a pilot programme to be introduced from 3 April 2017, the charge for pay-to-park bays during normal parking hours will be raised specifically within F zone for diesel cars, some of the heaviest of polluting vehicles. This will apply to visitors into Marylebone, with resident permits remaining unchanged.
The surcharge will add 50 per cent to the current rate of £4.90 per hour in F Zone. Customers are currently able to Park and Pay per minute up to a maximum of 240 minutes (4 hours), meaning charges will be 8p per minute in real terms and 12p per minute for diesels.
Marylebone suffers some of the highest pollution levels in London, given the area’s location, mix of land uses, building density and type, and number of vehicle trips. The ‘polluter pays’ principle aims to reduce harmful vehicle emissions in Marylebone and any money raised will be spent on initiatives to promote sustainable transport.
Marylebone’s location between major transport routes results in a complex urban air quality problem with levels of nitrogen dioxide that exceed recommended health levels and very high levels of particulate matter.
The council believes the pilot surcharge for diesel will also provide valuable insight into how the policy works practically and whether there are positive behavioural changes from it that could be replicated elsewhere.
In 2017, Westminster will also see several green initiatives come into effect in the low emission neighbourhood which will help improve air quality. This includes freight consolidation and a new EV infrastructure with charging points upgraded and increased by up to 20 new outlets, including some rapid chargers. The council is also encouraging more sustainable transport.