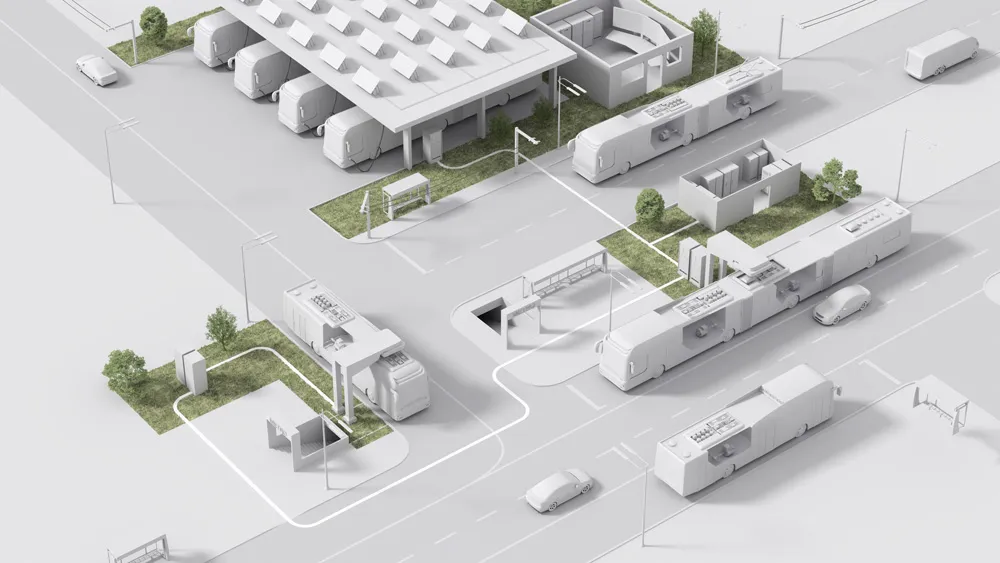
The world relies on commercial vehicle fleets. They are essential to business infrastructure in delivering industrial, commercial and private goods - but are coming under increasing pressure to curb their impact on the environment.
Commercial vehicles are moving towards electrification to create a long-term sustainable business advantage, reduce greenhouse gas emissions and comply with government regulations. These range from clean-air pollution control to banning noxious diesel trucks from operating in city centres.
Market studies have shown that medium-duty electric vehicles (EVs) will be cost-competitive with their fossil fuel counterparts in the next two years. Nevertheless, operators hesitate because electrification requires significant initial capital expenditure - for the EVs themselves, for related electrification infrastructure and for the cost of electricity from the grid.
The complexity is then multiplied across the entire industry and organisations struggle to make informed decisions around when and how best to adopt EVs. The solutions can be found through connectivity, the power of the industrial Internet of Things (IoT) and generating valuable data insights.
Data power
To enable fleet electrification we need digital solutions which provide a comprehensive view of business ecosystems and data-driven performance indicators. These can then simplify, clarify and profitably optimise all infrastructure design options and operational variables in an EV fleet conversion journey. These digitally informed solutions will mean fleets can make the change to EVs, significantly reducing their impact on the environment and their expenditure.
ABB has the largest installed base of EV fast chargers in the world, which gives us a great position to provide data-powered digital insight and solutions. We work with partners like parcel delivery group UPS to take on the challenge of digitising electrification.
The UPS depot in San Diego, California, is 18,500m2 and handles 125,000 packages per shift (at peak times) with a fleet of roughly 260 medium-duty internal combustion engine (ICE) trucks. ABB’s data suite can control operating cost per mile and enable profitable new business models. This can both reduce total cost of ownership and optimise capital expenditure in an electric fleet operation.
The ABB FleetGrid for UPS solution modelling began with an analysis, after introducing 32 EVs (each with an 80kWh battery) into the operation. This mirrors a typical phased approach, in the journey of fleet electrification, in which ICE trucks are usually replaced by EVs when they reach the end of their service lives.
The model-based simulation exercise proved that a data-informed implementation at the logistics depot would generate initial savings of $300,000 per year with this initial batch of EVs, growing to depot-wide savings of $2.5 million per year after a total conversion of the 260-vehicle ICE fleet at the depot.
Digital view
Businesses have been operating in the dark – but by plugging in at every data point they can gain a complete view of their operation in interpreted data. They can take decisions based on near real-time operational variables, everything from vehicle charging rate to type and size of infrastructure. Instead of simply taking on EVs as required, organisations can take decisions based on a comprehensive account of the business and supply chain, including when and how to adopt EVs with optimum business impact.
Comprehensive data-informed digital solutions can deliver success, reducing cost and negative impact on our environment. This means timely EV charging with the lowest cost of energy, beneficial cost-per-mile, on-time deliveries that satisfy service- level agreements and proper management of electric grid interactions, all executed with the lowest feasible CO2 emissions.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR:
Rob Massoudi is senior vice president, digital transformation, at ABB Ability








