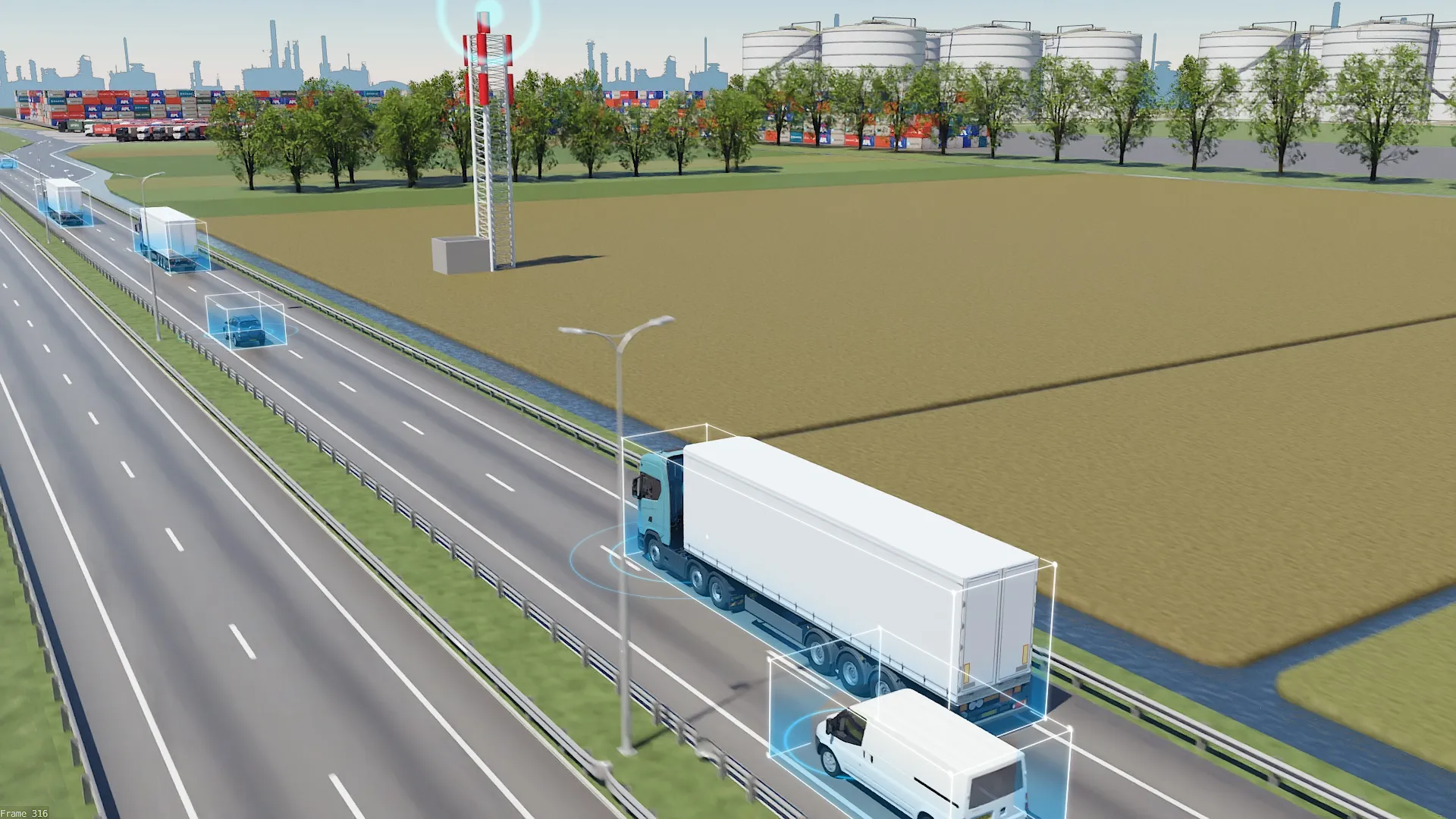
The international Celtic Plus Co-operative Mobility Services of the Future (CoMoSeF) project which, involved the development of data exchange between vehicles and infrastructure, has just presented its findings. The resulting communication system provides drivers with real time information on road weather, road conditions and incidents.
During the project a cooperative roadside weather monitoring station run by the Finnish Meteorological Institute relays the latest reports – and weather updates covering
July 1, 2015
Read time: 3 mins
The international Celtic Plus Co-operative Mobility Services of the Future (CoMoSeF) project which, involved the development of data exchange between vehicles and infrastructure, has just presented its findings. The resulting communication system provides drivers with real time information on road weather, road conditions and incidents.
During the project a cooperative roadside weather monitoring station run by the Finnish Meteorological Institute relays the latest reports – and weather updates covering larger road areas – to vehicles in the vicinity, using short-range WLAN-based ITS-G5 technology and the mobile phone network. This data is received by a vehicle system developed by814 VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland. The system can receive multichannel data either via ITS-G5 mediating between vehicles, or the mobile phone network. The switch from one signal reception technology to another is so fast that there are no breaks in contact with the station.
Data transfer techniques of this kind, which seamlessly combine several radio systems, have recently emerged as a potential model for the ITS solutions of the future.
”As it proliferates, cooperative driving based on communication and data exchange between vehicles and road network systems will noticeably improve traffic safety,” says Johan Scholliers principal scientist at VTT.
Cooperative traffic systems will extend the electronic horizon of vehicles, so that drivers can prepare in advance for hazards which they know are lurking behind corners. This will help drivers and vehicles to anticipate traffic more effectively and to decide accordingly on issues such as the right speed and choice of route.
These solutions represent a step towards automated, smart traffic. It is predicted that cooperative driving will be part of everyday life by the 2020s. One objective which is likely to accelerate uptake lies in markedly lowering the price of the required vehicle infrastructure.
One of the project's test sites has been the Hervanta feeder road and E63 exit ramp close to Tampere, where a cooperative road side unit with camera and laser scanner has been installed on the ramp for fog surveillance purposes. Another station relaying weather data to vehicles has been installed along the E75 road south of Sodankylä town centre.
In addition to Finland, intelligent traffic solutions and services have been developed and tested under the CoMoSeF project in France, Luxembourg, Romania, Spain, Turkey and South Korea, where road traffic faces different challenges to those of Finland.
The three-year CoMoSeF project was led by the Tampere company DDS/Mobisoft which, in addition to project coordination, gathers real-time traffic information from taxis in the city and relays processed traffic and road condition information to in-vehicle devices in taxis. Finnish participants included the Finnish Meteorological Institute, VTT, Infotripla, Taipale Telematics and Centria. There were also enterprises and research institutions from six other countries: France, Spain, Luxembourg, Romania, Turkey and South Korea.
During the project a cooperative roadside weather monitoring station run by the Finnish Meteorological Institute relays the latest reports – and weather updates covering larger road areas – to vehicles in the vicinity, using short-range WLAN-based ITS-G5 technology and the mobile phone network. This data is received by a vehicle system developed by
Data transfer techniques of this kind, which seamlessly combine several radio systems, have recently emerged as a potential model for the ITS solutions of the future.
”As it proliferates, cooperative driving based on communication and data exchange between vehicles and road network systems will noticeably improve traffic safety,” says Johan Scholliers principal scientist at VTT.
Cooperative traffic systems will extend the electronic horizon of vehicles, so that drivers can prepare in advance for hazards which they know are lurking behind corners. This will help drivers and vehicles to anticipate traffic more effectively and to decide accordingly on issues such as the right speed and choice of route.
These solutions represent a step towards automated, smart traffic. It is predicted that cooperative driving will be part of everyday life by the 2020s. One objective which is likely to accelerate uptake lies in markedly lowering the price of the required vehicle infrastructure.
One of the project's test sites has been the Hervanta feeder road and E63 exit ramp close to Tampere, where a cooperative road side unit with camera and laser scanner has been installed on the ramp for fog surveillance purposes. Another station relaying weather data to vehicles has been installed along the E75 road south of Sodankylä town centre.
In addition to Finland, intelligent traffic solutions and services have been developed and tested under the CoMoSeF project in France, Luxembourg, Romania, Spain, Turkey and South Korea, where road traffic faces different challenges to those of Finland.
The three-year CoMoSeF project was led by the Tampere company DDS/Mobisoft which, in addition to project coordination, gathers real-time traffic information from taxis in the city and relays processed traffic and road condition information to in-vehicle devices in taxis. Finnish participants included the Finnish Meteorological Institute, VTT, Infotripla, Taipale Telematics and Centria. There were also enterprises and research institutions from six other countries: France, Spain, Luxembourg, Romania, Turkey and South Korea.