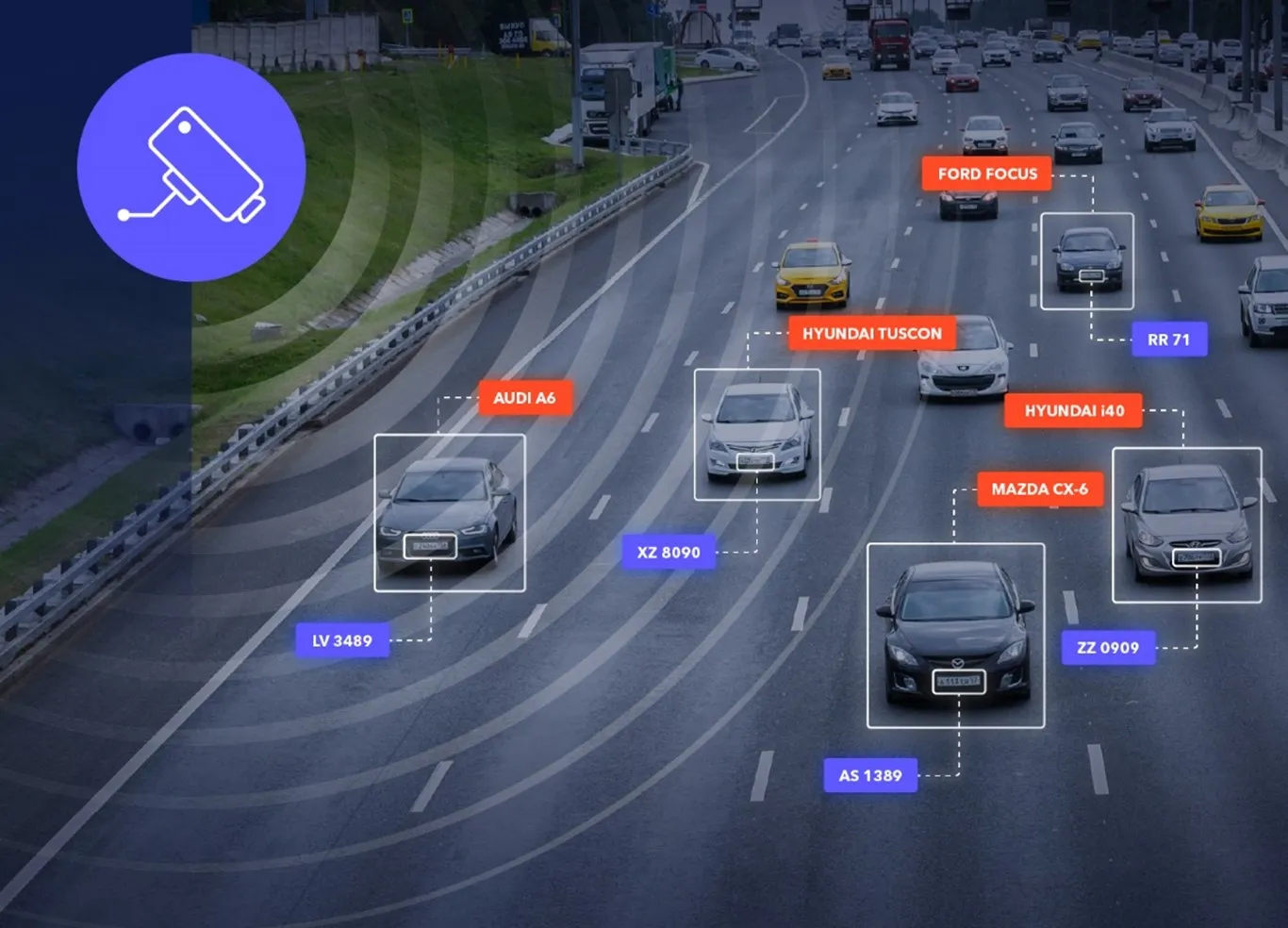
The Road Safety Markings Association (RSMA) has responded to the UK government’s announcement giving driverless cars the go-ahead on UK roads, saying that it points to an exciting future, but hampered at the outset by the daily routine of road works, potholes, worn road markings, burst mains and failed traffic lights.
“By 2025, at least half the travel on Europe’s roads will be in vehicles that can read the road ahead including markings and signs. But vehicles, like drivers, cannot function if basic road markings and signs are non-existent, non-compliant, worn out, obscured, inconsistent or confusing,” says George Lee, national director of the RSMA.
“In spite of the best efforts of local authorities and utility companies, road works are frequently chaotic, and difficult to negotiate for even the most experienced driver.
“We know from our own extensive survey of the UK’s local and national road network that half of markings need replacing immediately or scheduled for replacing.
“Poor maintenance and worn and inconsistent road markings and traffic signs are now a major obstacle to the effective use of technology in vehicles, such as lane departure warning and traffic sign recognition.
“The prospect of self-driving cars is exciting; the reality of cars that can read roads is already with us; but it would be a huge step forward if we could have roads that can be read easily by humans – who still account for the vast majority of road users,” says Lee.
“Chaotic” roads will stall self-driving cars
The Road Safety Markings Association (RSMA) has responded to the UK government’s announcement giving driverless cars the go-ahead on UK roads, saying that it points to an exciting future, but hampered at the outset by the daily routine of road works, potholes, worn road markings, burst mains and failed traffic lights.
“By 2025, at least half the travel on Europe’s roads will be in vehicles that can read the road ahead including markings and signs. But vehicles, like drivers, cannot function if basic road
July 31, 2014
Read time: 2 mins