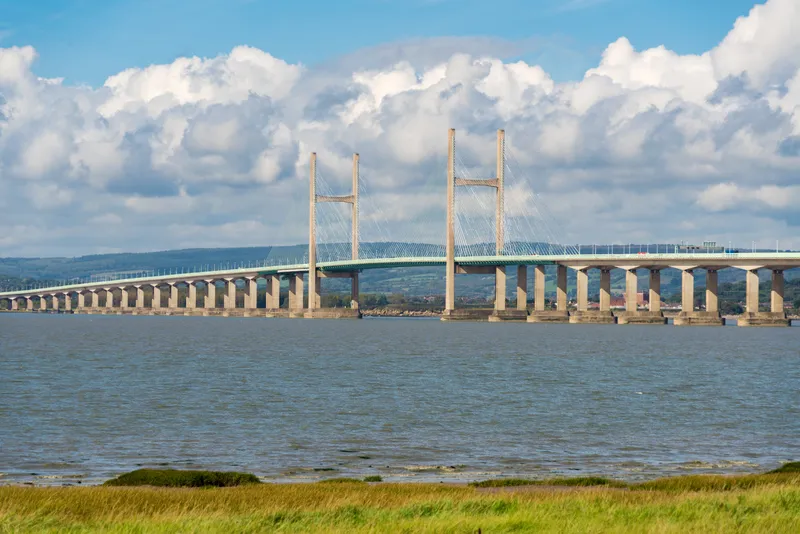
The German government has introduced a controversial road toll which will force foreign car drivers to pay up to €130 (US$162) a year for using Germany's autobahn motorways.
The plan, intended to help the country fund the upkeep of its transport infrastructure which is used by millions of foreign vehicles, may yet face a legal challenge in Brussels for discriminating against foreign motorists.
After months of heated debate between Chancellor Angela Merkel's Christian Democrats (CDU) and their Bavarian sister party Christian Social Union (CSU), Transport Minister Alexander Dobrindt dropped an original idea to raise the fee on all roads.
However, he stuck to the plan that the toll will not lead to extra costs for German drivers by allowing them to offset the levy against an already existing motor vehicle tax. Dobrindt, a leading member of the CSU, said he was convinced that his draft law does not discriminate against foreign motorists and therefore would stand if challenged in court.
“The infrastructure fee is sensible, fair and just,” the minister said, adding that the revenues of the toll would only be used to modernise Germany’s motorways and main roads.
The toll is expected to be introduced in 2016. Motorists have to register their vehicle details via the internet. Foreign drivers can also pay the levy at petrol stations. The fee will take into account the vehicle’s cylinder capacity and environmental compatibility with a maximum toll of €130 a year. Foreign drivers can pay a ten-day levy for €10 (US$13) or two month for €22 (US$27).
Dobrindt’s CSU wants foreign motorists to pay tolls on motorways because they think it is unfair that foreigners travel for free in Germany while German drivers have to pay tolls in neighbouring countries like Austria, Switzerland and France.
The CSU pressed the motorway toll issue in coalition talks after last year’s German federal elections. But Merkel’s CDU and its other coalition ally, the centre-left Social Democrats (SPD), said they would only back the toll if it did not lead to extra costs for German motorists and if it complied with
Germany has already introduced a satellite-based toll system for lorries that obliges truck drivers to pay on motorways. This toll depends on the number of kilometres actually driven.
German road toll to cost foreign drivers up to €130 a year
The German government has introduced a controversial road toll which will force foreign car drivers to pay up to €130 (US$162) a year for using Germany's autobahn motorways.
November 3, 2014
Read time: 2 mins